The property hierarchy in res:harmonics represents the property information that covers you property portfolio.
The following give a high level overview of the hierarchy -
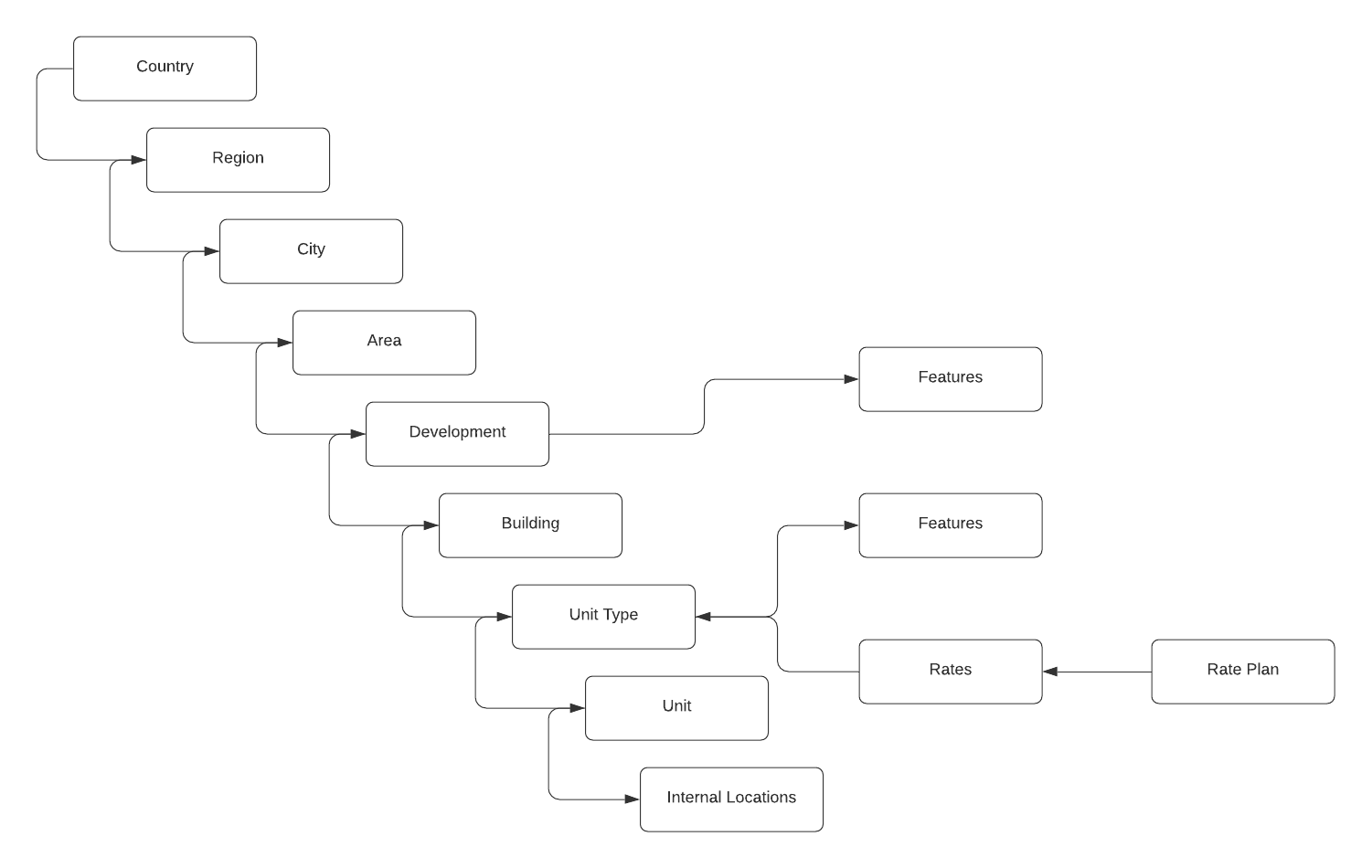 Addressing the property data in alphabetical order -
Addressing the property data in alphabetical order -
Area: Represents a specific neighborhood or zone within a city where the property is located. It provides finer granularity in identifying the property’s location beyond just the city level. Areas can often influence the property’s value or appeal due to factors like amenities, proximity to landmarks, or local culture.
Building: Refers to an individual structure within a development. A single development may contain multiple buildings, each with unique characteristics, features, and potentially distinct rates or units. Buildings serve as physical containers for units, such as apartments, storage spaces, or parking spots.
City: Identifies the urban area within a region where the property resides. This is a broader geographical grouping used to organize properties by metropolitan boundaries, population centers, or economic zones. Cities often influence property demand and pricing due to their infrastructure, employment opportunities, and population density.
Country: Represents the nation where the property is located. The country level is the highest geographic tier and is often used for international operations, ensuring properties are classified within appropriate legal, tax, and cultural boundaries.
Development: Serves as a marketing or organizational container for a group of properties within a specific area or region. A development often represents a cohesive real estate project, such as a residential estate, a commercial complex, or a mixed-use community. It includes branding, shared amenities, and infrastructure.
Feature/Facility: Describes specific attributes, amenities, or facilities available within a development, building, or unit. Examples include a swimming pool, gym, concierge service, or parking garage. Features enhance the property’s value and appeal to prospective tenants or buyers.
Rate Plan: Acts as an overarching pricing framework used to group and manage similar rates for a property. A rate plan might cover seasonal pricing, promotional discounts, or standard rates for daily, weekly, or monthly stays. It ensures consistency and simplifies rate management across multiple units or unit types.
Rate: Represents the actual pricing for a unit type on a daily, monthly, or other periodic basis. Rates may vary depending on factors such as occupancy, seasonality, or unit features. Rates are directly tied to unit types, ensuring pricing reflects the characteristics and value of each grouping.
Region: Refers to a broader area within a country that includes multiple cities or towns. Regions may align with administrative boundaries, such as states, provinces, or counties, and serve as an intermediate tier between cities and countries. They help organize properties geographically and may influence market trends or regulations.
Unit Type: Groups similar units within a building by shared characteristics, such as layout, size, or intended use. Examples include one-bedroom apartments, two-bedroom apartments, or studio flats. Unit types simplify the process of categorizing and pricing units with similar attributes.
Unit: Represents an individual space within a building, such as an apartment, storage unit, or parking space. Each unit is unique and may have its own features, rates, and internal locations. Units are the smallest rentable or sellable entities in the hierarchy.
Unit Internal Location: Links a unit to specific internal locations within it. For example, a two-bedroom apartment might include internal locations such as Bedroom 1, Bedroom 2, and Kitchen. This layer allows for detailed mapping of the unit’s internal structure.
Internal Location: Represents specific areas or spaces within a unit, such as individual rooms, closets, or balconies. This level of detail is helpful for planning layouts, showcasing features, or managing maintenance and operations.